|
|
|
Kindle Available The Missouri Compromise and Its Aftermath: Slavery and the Meaning of America Go behind the scenes of the crucial Missouri Compromise, the most important sectional crisis before the Civil War, the high-level deal-making, diplomacy, and deception that defused the crisis. The Robert E Lee Family Slaves |
On January 29, 1850, the 70-year-old Henry Clay, U.S. senator from Kentucky, presented a compromise. For eight months members of Congress, led by Clay, Daniel Webster, Senator from Massachusetts, and John C. Calhoun, senator from South Carolina, debated the compromise. With the help of Stephen Douglas, a young Democrat from Illinois, a series of bills that would make up the compromise were ushered through Congress. According to the compromise, Texas would relinquish the land in dispute but, in compensation, be given 10 million dollars -- money it would use to pay off its debt to Mexico. Also, the territories of New Mexico, Nevada, Arizona, and Utah would be organized without mention of slavery. (The decision would be made by the territories' inhabitants later, when they applied for statehood.) Regarding Washington, the slave trade would be abolished in the District of Columbia, although slavery would still be permitted. Finally, California would be admitted as a free state. To pacify slave-state politicians, who would have objected to the imbalance 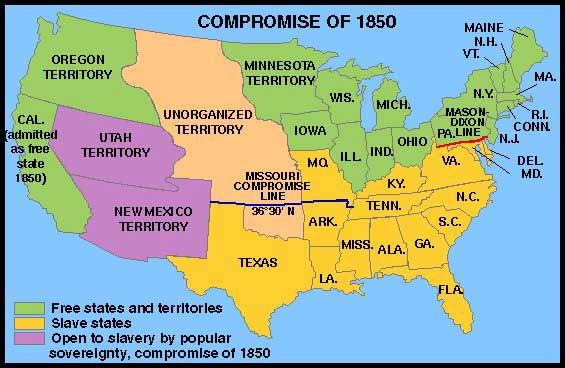 created by adding another free state, the Fugitive Slave Act was passed. created by adding another free state, the Fugitive Slave Act was passed. Of all the bills that made up the Compromise of 1850, the Fugitive Slave Act was the most controversial. It required citizens to assist in the recovery of fugitive slaves. It denied a fugitive's right to a jury trial. (Cases would instead be handled by special commisioners -- commisioners who would be paid $5 if an alleged fugitive were released and $10 if he or she were sent away with the claimant.) The act called for changes in filing for a claim, making the process easier for slaveowners. Also, according to the act, there would be more federal officials responsible for enforcing the law. For slaves attempting to build lives in the North, the new law was disaster. Many left their homes and fled to Canada. During the next ten years, an estimated 20,000 blacks moved to the neighboring country. For Harriet Jacobs, a fugitive living in New York, passage of the law was "the beginning of a reign of terror to the colored population." She stayed put, even after learning that slave catchers were hired to track her down. Anthony Burns, a fugitive living in Boston, was one of many who were captured and returned to slavery. Free blacks, too, were captured and sent to the South. With no legal right to plead their cases, they were completely defenseless. Passage of the Fugitive Slave Act made abolitionists all the more resolved to put an end to slavery. The Underground Railroad became more active, reaching its peak between 1850 and 1860. The act also brought the subject of slavery before the nation. Many who had previously been ambivalent about slavery now took a definitive stance against the institution. The Compromise of 1850 accomplished what it set out to do -- it kept the nation united -- but the solution was only temporary. Over the following decade the country's citizens became further divided over the issue of slavery. The rift would continue to grow until the nation itself divided. |
 Henry Clay Statesman for the Union |
 Henry Clay Arguing in the Us Senate for the Compromise of 1850 to Avert Civil War 16 in. x 12 in. Buy at AllPosters.com |
Dred Scott
Civil War Picture Album
Crittenden Compromise 1860
American Civil War Exhibits
Civil War Timeline
Women in the War
State Battle Maps
Ships and Naval Battles
Civil War Summary
 Slavery, Secession, and Civil War Views from the UK and Europe, 1856-1865 Contains articles written by foreign journalists living in the UK and Europe during the American Civil War, who provide an outsider's view of events. Articles were first published from 1856-1865 in British, French, and Spanish journals |
 Bitter Fruits Of Bondage: The Demise Of Slavery And The Collapse Of The Confederacy, 1861-1865 The process of social change initiated during the birth of Confederate nationalism undermined the social and cultural foundations of the southern way of life built on slavery, igniting class conflict that ultimately sapped white southerners of the will to go on. |
 Prelude to Civil War: The Nullification Controversy in South Carolina From 1816 to 1836 planters of the Palmetto State tumbled from a contented and prosperous life to a world rife with economic distress, guilt over slavery, and apprehension of slave rebellion. Compelling details ofhow this reversal of fortune led the political leaders down the path to states rights doctrines |
 A House Divided: The Antebellum Slavery Debates in America, 1776-1865 An excellent overview of the antebellum slavery debate and its key issues and participants. The most important abolitionist and proslavery documents written in the United States between the American Revolution and the Civil War |
 To 'Joy My Freedom: Southern Black Women's Lives and Labors after the Civil War Thousands of former slaves flocked to southern cities in search of work, they found the demands placed on them as wage-earners disturbingly similar to those they had faced as slaves: seven-day workweeks, endless labor, and poor treatment |
Kindle Available Many Thousands Gone: The First Two Centuries of Slavery in North America The evolution of black society from the first arrivals in the early seventeenth century through the Revolution |
Kindle Available Political Culture and Secession in Mississippi: Masculinity, Honor, and the Antiparty Tradition, 1830-1860 A rich new perspective on the events leading up to the Civil War and will prove an invaluable tool for understanding the central crisis in American politics. |
Kindle Available Nothing but Freedom Emancipation and Its Legacy Insights into the relatively neglected debates over fencing laws and hunting and fishing rights in the postemancipation South, and into the solidarity of the low-country black community |
 Freedom Train: The Story of Harriet Tubman Harriet escaped North, by the secret route called the Underground Railroad. Harriet didn't forget her people. Again and again she risked her life to lead them on the same secret, dangerous journey. |
Kindle Available The Glory Cloak: A Novel of Louisa May Alcott and Clara Barton From childhood, Susan Gray and her cousin Louisa May Alcott have shared a safe, insular world of outdoor adventures and grand amateur theater -- a world that begins to evaporate with the outbreak of the Civil War. Frustrated with sewing uniforms and wrapping bandages, the two women journey to Washington, D.C.'s Union Hospital to volunteer as nurses. |
 Clara Barton Founder of the American Red Cross Young Clara Barton is shy and lonely in her early days at boarding school. She is snubbed by the other girls because she doesn't know how to talk to them. But when she gets an opportunity to assist the local doctor, her shyness disappears, and Clara begins to discover her true calling as a nurse. |
 Grace's Letter to Lincoln Many important details of the time period help to make the reader understand what life was like then. It also includes photos of the actual letters written between Grace and Mr. Lincoln |
 Allen Jay and the Underground Railroad Allen Jay and the Underground Railroad is the retelling of a man's recollections of his first experience helping an escaped slave. The book brings the underground railroad down to the level primary students can comprehend. This book makes for wonderful discussions regarding overcoming one's fears, going against the norm and doing what you believe to be morally correct. |
 Numbering The Bones The Civil War is at an end, but for thirteen-year-old Eulinda, it is no time to rejoice. Her younger brother Zeke was sold away, her older brother Neddy joined the Northern war effort,. With the help of Clara Barton, the eventual founder of the Red Cross, Eulinda must find a way to let go of the skeletons from her past. |
 Night Boat To Freedom Night Boat to Freedom is a wonderful story about the Underground Railroad, as told from the point of view of two "ordinary" people who made it possible. Beyond that, it is a story about dignity and courage, and a devotion to the ideal of freedom. |
 Voice of Freedom A Story About Frederick Douglass Interesting for both children and adults, this book does much to evoke the strong-minded, highly-principled person who inspired so many others |
 Bad Blood: The Border War That Triggered the Civil War In the years leading up to the Civil War, a bloody conflict between slaveholders and abolitionists focused the nation's eyes on the state of Missouri and the territory of Kansas. Told through the actual words of slave owners, free-staters, border ruffians, and politicians, Bad Blood presents the complex morality, differing values, and life-and-death decisions faced by those who lived on the Missouri-Kansas border |
 Blue Vs. Gray - Killing Fields Relive the most vicious fighting of the Civil War, in which General Ulysses S. Grant forcibly reversed the tide of the conflict by paying with the blood of thousands. It was a desperate time for the Union |
 Civil War Combat: America's Bloodiest Battles The violent mayhem of the hornet's nest at Shiloh, the valiant charge on the sunken road at Antietam, the carnage in the wheat field at Gettysburg, and the brutal fighting at Cold Harbor |
 Jefferson Davis An American President One of the most outstanding statesmen of the United States during the first 60 years of the 19th century, he sacrificed everything to defend the South's position regarding the rights of the states and conservative constitutional interpretation. Against staggering odds he led the South and held it together in the bloody Civil War or War Between the States |
| Search AmericanCivilWar.com |
| Enter the keywords you are looking for and the site will be searched and all occurrences of your request will be displayed. You can also enter a date format, April 19,1862 or September 1864. |