The USS Monitor represented a revolution in warship design. Not only was the vessel fully armored, but she mounted her guns in a revolving turret, which in theory was capable of firing in any direction. Following the first fight between two ironclads at the Battle of Hampton Roads (March 9, 1862) the North was swept by "monitor fever," as everyone from President Lincoln down became convinced that victory in the naval war would be achieved through the creation of a fleet of "monitor" ironclads. The original USS Monitor therefore spawned a host of successors, and gave her name to a new type of warship.
On March 14, 1861, Gideon Wells became President Lincoln's Secretary of the Navy. A month later the country was irrevocably plunged into war. When Lincoln approved the "Anaconda Plan," devised by General Winfield Scott, he committed his navy to a course for which it was ill-prepared. The strategy envisaged the encirclement of the Confederacy by both a naval blockade of Southern ports and a drive down the Mississippi River. Scotts' Anaconda would constrict his victim, squeezing the life out of the Confederacy by applying pressure to its borders.
When the war was declared in April 1861 the US Navy had just over 90 warships at its disposal, but 48 were either in refit or were unfit for service, and another 28 vessels were deployed overseas. The remaining vessels were clearly insufficient to put into effect any blockade of the Confederate coast, so Welles instituted a huge expansion of the fleet. This included the aquisition and conversion of merchant ships until new purpose-built vessels could be constructed. He also considered the consttruction of armored warships. Both Welles and his Confederate counterpart were aware of the introduction of ironclad warships into the French and British fleets. During 1861 Welles became increasingly convinced that his naval plans would necessarily involve the adoption of a new breed of ironclad warships.
Copyright Osprey Publishing
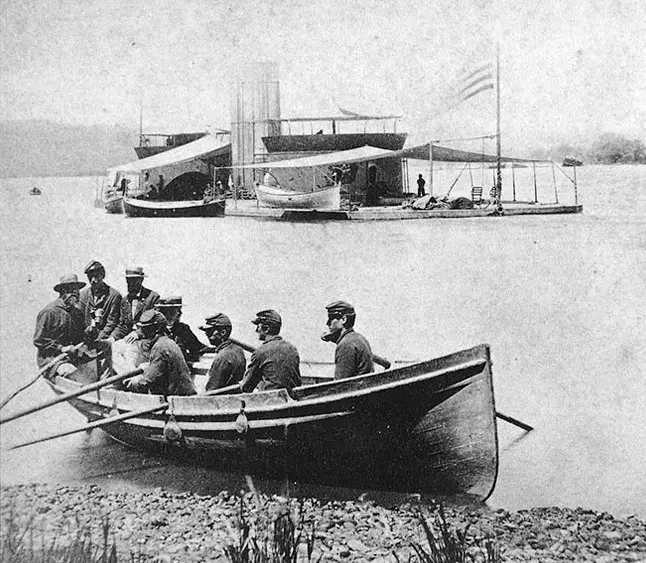
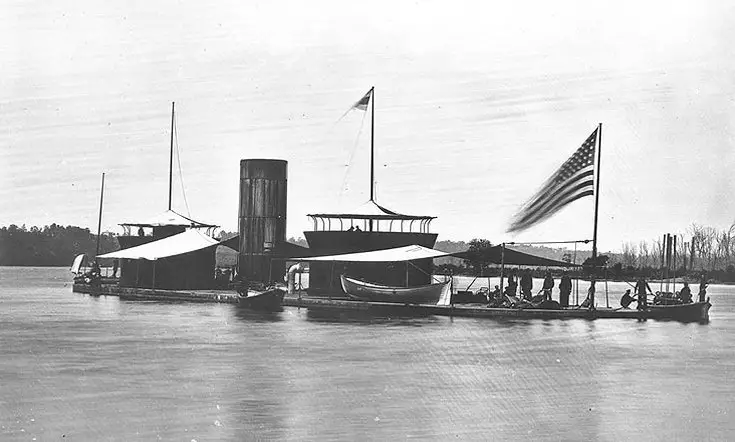
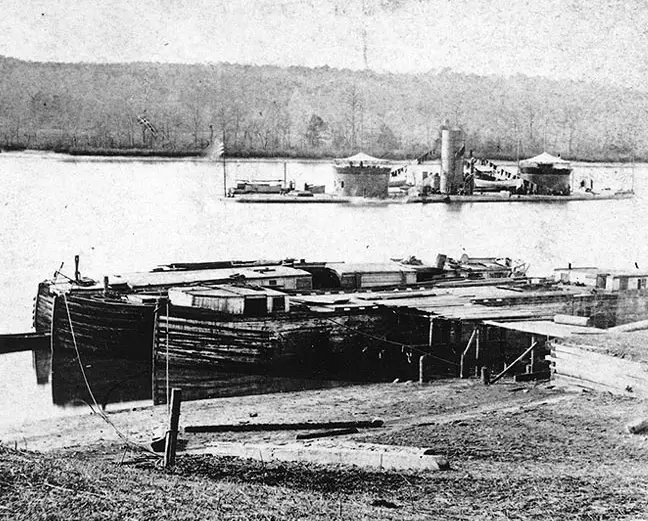
USS Onondaga anchor on the James River, Virginia, during the Civil War, circa 1864-65.
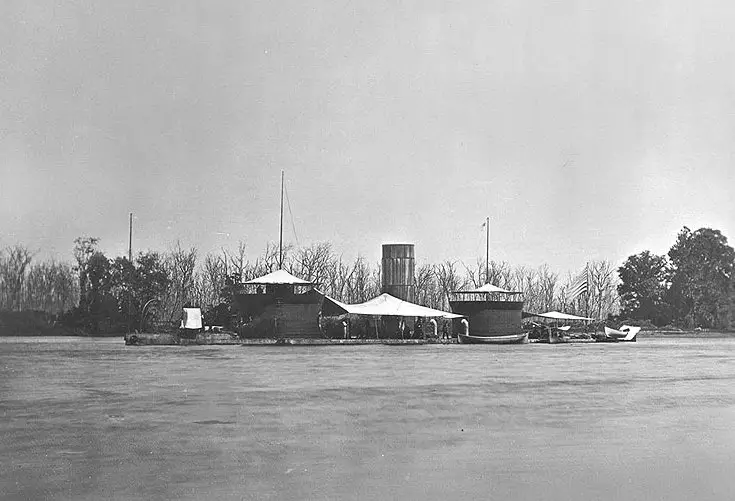

USS Onondaga Anchored off Aikens Landing in the James River, Virginia, in 1864-1865. Note the barges at the wharf in the foreground.
Aikens Landing, near Dutch Gap, was the site of prisoner of war exchanges.


Raising the Hunley: The Remarkable History and Recovery of the Lost Confederate Submarine
For more than a century the fate of the Hunley remained one of the great unsolved mysteries of the Civil War. Then, on August 8, 2000, with thousands of spectators crowding Charleston Harbor, the Hunley was raised from the bottom of the sea and towed ashore.

Year on a Monitor and the Destruction of Fort Sumter
Personal view of the Civil War Navy. The monitor saw action in several significant naval assaults by the Union's Squadron. It took part in the failed Federal attack on Sumter in April 1863. The "Nahant" also participated in the capture of the Confederate Ram "Atlanta," and in the assault on Fort Wagner