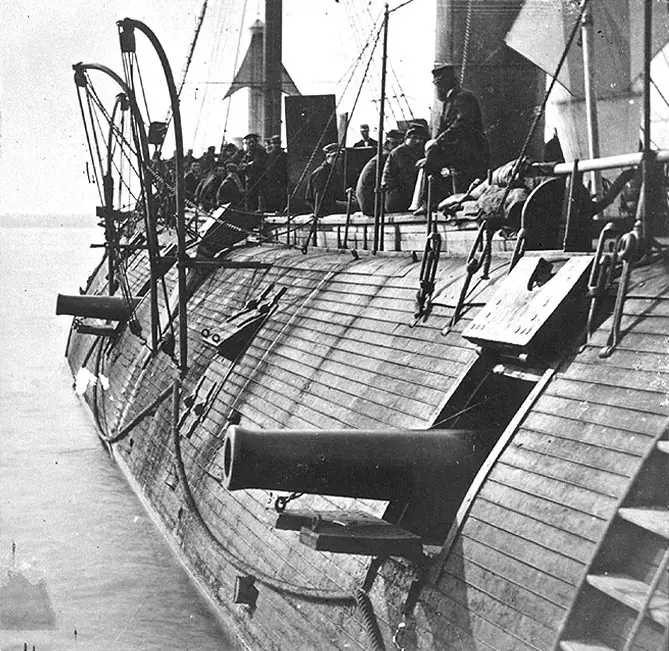
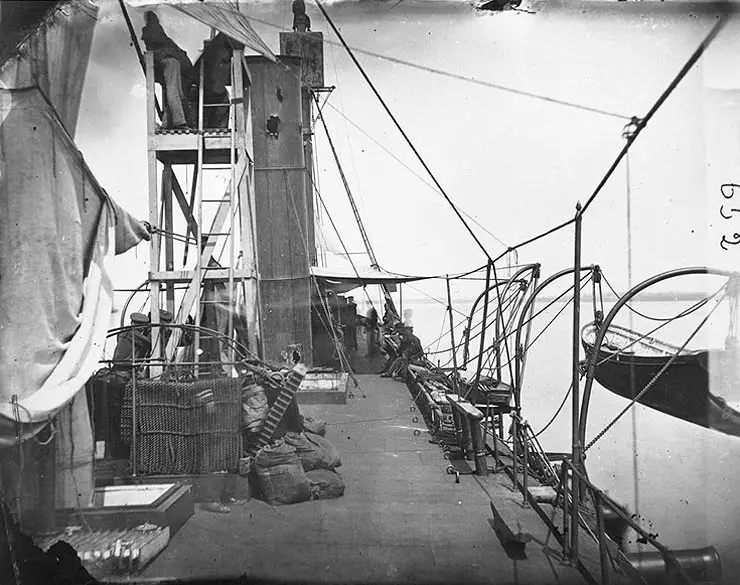
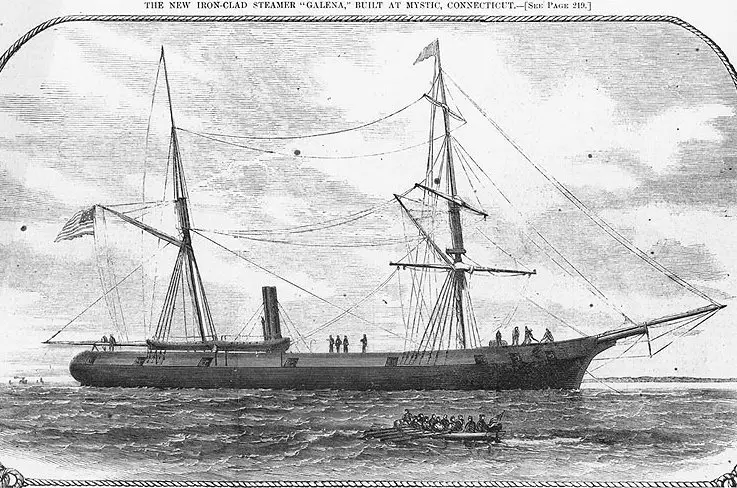
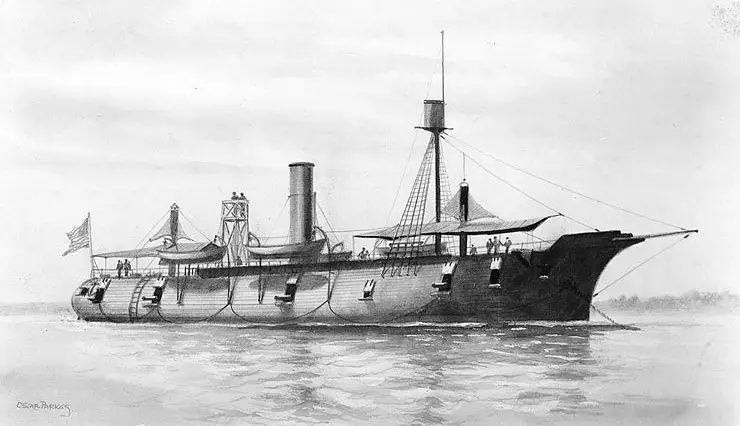
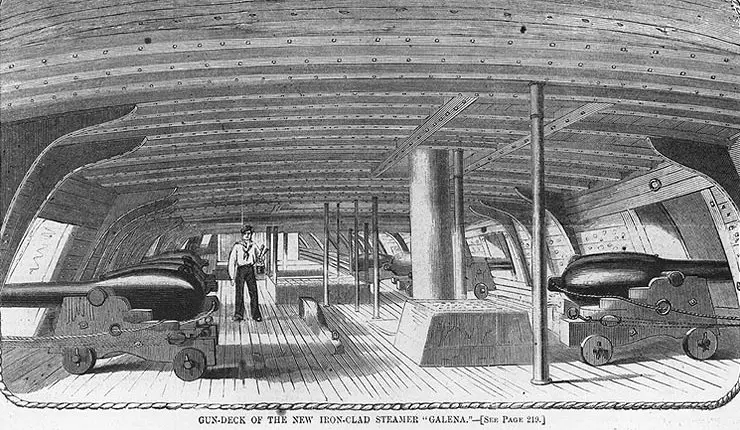
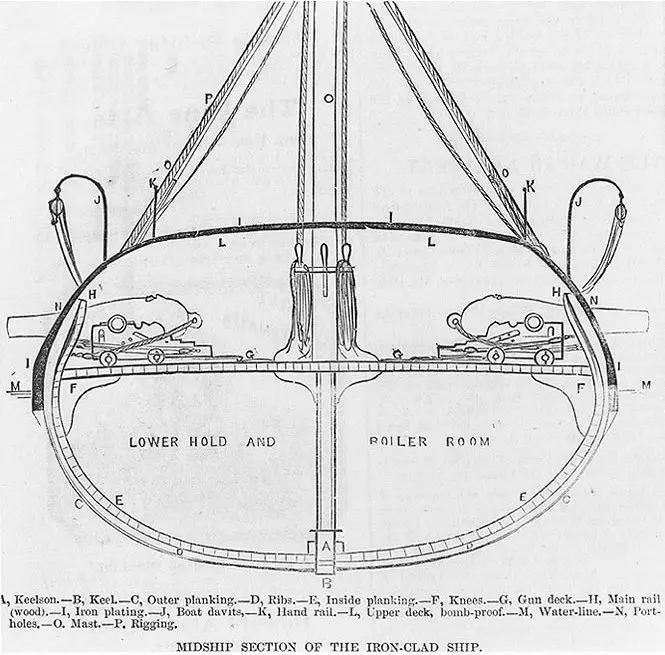
USS Galena , a 950-ton ironclad gunboat, was built at Mystic, Connecticut. Commissioned in April 1862 as the second of the U.S. Navy's first three armored warships, she was immediately sent to Hampton Roads, Virginia, to join the Navy's pioneer ironclad Monitor in containing CSS Virginia . On 8 May, Galena attacked enemy shore batteries on the James River, part of an intended drive up the river to take Richmond, the Confederate capital city.
After the Virginia was destroyed, Galena and other Union warships steamed up the James on 15 May to bombard Fort Darling, located at Drewry's Bluff about eight miles below Richmond. In a sharp action, Confederate gunners badly damaged Galena , killing twelve of her crew and demonstrating the inadequacy of her relatively thin iron armor. Despite her injuries, the ship remained in the James River area through the next four months, shelling enemy shore positions on several occasions in support of General McClellan's army during the flow and ebb of its campaign on the Virginia Peninsula. After Galena left the James in September 1862, she was stationed in Hampton Roads until May 1863, when she went to Philadelphia for repairs and alterations.
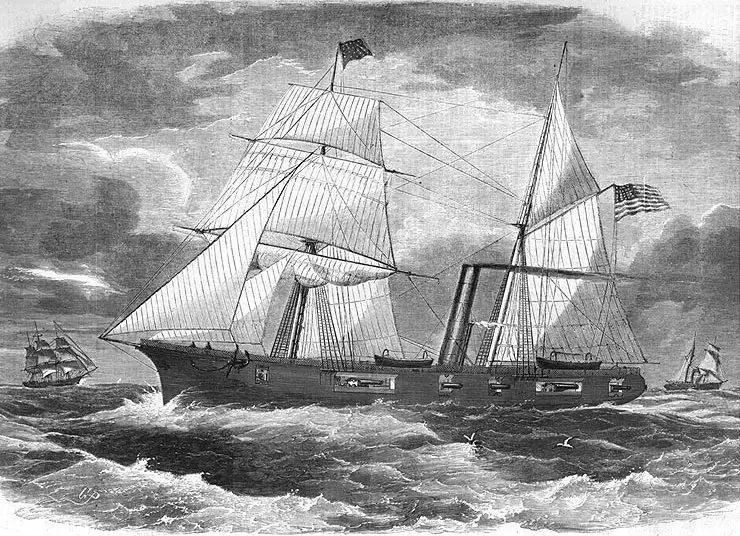
Recommissioned in February 1864, Galena had been stripped of her iron plating, given a heavier gun battery and enlarged sail rig. Now a conventional unarmored steam warship, in May she joined the West Gulf Blockading Squadron's pending assault on Mobile Bay, Alabama. She was one of the ships that ran past the Bay's defending Fort Morgan on the morning of 5 August 1864. During that action, she assisted USS Oneida to safety after that ship was disabled by Confederate gunfire. Later in the month, Galena took part in the siege that led to Fort Morgan's surrender.
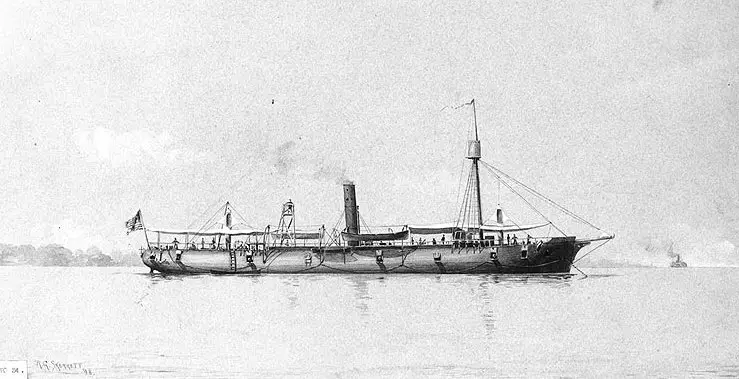
Galena served in the East Gulf Blockading Squadron in September-November 1864. After four months of shipyard repairs, she served on Virginia's James and Nansemond Rivers through the end of the Civil War. She decommissioned in June 1865 and was thereafter inactive except for a brief time in the spring of 1869. USS Galena was broken up in 1872 at the Norfolk Navy Yard, where a new and somewhat larger Galena was built under the administrative fiction of repairing the original.

Wolf of the Deep: Raphael Semmes and the Notorious Confederate Raider CSS Alabama
In July 1862, the Confederate captain Raphael Semmes received orders to report to Liverpool, where he would take command of a secret new British-built steam warship. His mission: to prey on Union commercial vessels and undermine the North's ability to continue the war